|
|
|
|
|
|

|
UE: Application IP stack queues up IP packets for transmission. UL-TFTf maps IP packets to appropriate DRB.
eNB: User data queues would be tunnels coming from GTP-U entity (one tunnel per one DRB).
In our example we have two bearers (one, of course, default and the other dedicated).
|
|

|
PDCP compresses IP/UDP/RTP header, which result into reduced payload. This is a major saving as PDCP can compress header from 40 bytes to upto 2 bytes [rfc3095] !!
|
|
|
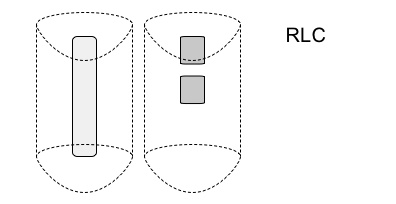
Three chunks of data that were injected into LTE stack, till RLC remain as three separate chunks. From RLC onwards, these chunks are split and/or concatenated as per dynamic radio conditions - to achieve best possible transmission ! RLC PDU size (and so number of RLC PDUs) is not known till "transmission opportunity" is notified by MAC [36.322:4.2.1.3.2, 4.3.2].
In the example, first two SDUs are concatenated and third SDU is segmented.
|
|

|
LTE Transport format - interface between MAC and PHY - support one transport block in one TTI (2 TBs in case of spatial multiplexing/MIMO). The TB size is decided based on dynamic radio conditions by eNode B MAC/PHY and conveyed to UE through PHY signaling. This procedure is nothing but "resource assignment or allocation" procedure. TB size decision is made by eNB MAC scheduler. MAC controls PHY operation and depending on determined TB size informs about "transmission opportunity" to RLC.
|
|

|
In our example, MAC has multiplexed two RLC PDUs in one TB, next TB has only one RLC PDU. Needless to say, TB size vary from TTI to TTI.
If "Transport" representation of allocation is "transport block size", "Physical" representation would be "resource blocks".
With the help of 1) PHY signaling information - like IMCS (Modulation & Coding Scheme index), type of RNTI used for CRC scrambling - 2) System bandwidth in terms of resource blocks - NPRB - and 3) transport block size tables specified in TS 36.213, transport block size for a particular TTI is determined [36.213:7.1.7, 8.6]. PHY signaling also has details about resource blocks, which maps to time/frequency parameters.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|